MongoDB Documentation

MongoDB Documentation – There are several methods to update Document in MongoDB:
- updateOne: refreshes one document that meets the filtering criteria and returns information about the update operation
- updateMany: refreshes all documents that meet the filtering criteria and returns information about the update operation
- findOneAndUpdate: refreshes one document that meets the filter criteria and returns an updated document.
findOneAndUpdate
The findOneAndUpdate() method updates one element. It accepts the following parameters:
- The criterion for filtering the document to be updated
- Update option
- Additional update options, which are null by default
- The callback function that is performed during an update
For example, let’s update the first user in the database who is 21 years old:
const MongoClient = require("mongodb").MongoClient;
const url = "mongodb://localhost:27017/";
const mongoClient = new MongoClient(url, { useNewUrlParser: true });
let users = [{name: "Bob", age: 34} , {name: "Alice", age: 21}, {name: "Tom", age: 45}];
mongoClient.connect(function(err, client){
if(err) return console.log(err);
const db = client.db("usersdb");
const col = db.collection("usersdb");
col.insertMany(users, function(err, results){
col.findOneAndUpdate(
{age: 21}, // sampling criterion
{$set: {age: 25}}, // update parameter
function(err, result){
console.log(result);
client.close();
}
);
});
});
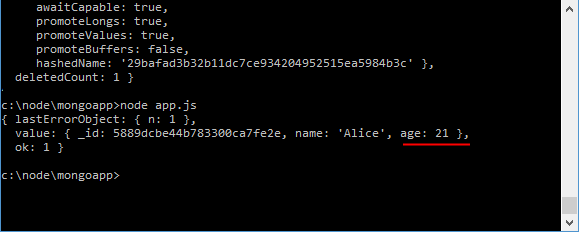
At first, 3 users shall be added to the database, and after the addition is updated.
The object { $set shall be used for updating: object {age: 25}}. The $set parameter shall update the values for a single field or group of fields. In this case, the age field shall be changed.
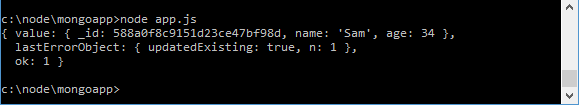
The third parameter, the callback function, displays the update result. By default, this is the old state of the modified document:
But, let’s say, after the update, we want to get not the old but the new state of the modified document. To do this, we can specify additional update options.
const MongoClient = require("mongodb").MongoClient;
const url = "mongodb://localhost:27017/";
const mongoClient = new MongoClient(url, { useNewUrlParser: true });
mongoClient.connect(function(err, client){
if(err) return console.log(err);
const db = client.db("usersdb");
const col = db.collection("usersdb");
col.findOneAndUpdate(
{name: "Bob"}, // sampling criterion
{$set: {name: "Sam"}}, // update parameter
{ // additional update options
returnOriginal: false
},
function(err, result){
console.log(result);
client.close();
}
);
});
updateMany
The updateMany() method allows you to update all documents in the collection that meet the filtering criteria:
const MongoClient = require("mongodb").MongoClient;
const url = "mongodb://localhost:27017/";
const mongoClient = new MongoClient(url, { useNewUrlParser: true });
mongoClient.connect(function(err, client){
if(err) return console.log(err);
const db = client.db("usersdb");
const col = db.collection("usersdb");
col.updateMany(
{name: "Sam"}, // filter criterion
{$set: {name: "Bob"}}, // update parameter
function(err, result){
console.log(result);
client.close();
}
);
});
updateOne
The updateOne() method is similar to the updateMany method except that it updates only one element. Unlike the findOneAndUpdate() method, it does not return a modified document:
const MongoClient = require("mongodb").MongoClient;
const url = "mongodb://localhost:27017/";
const mongoClient = new MongoClient(url, { useNewUrlParser: true });
mongoClient.connect(function(err, client){
if(err) return console.log(err);
const db = client.db("usersdb");
const col = db.collection("usersdb");
col.updateOne(
{name: "Tom"},
{$set: {name: "Tom Junior", age:33}},
function(err, result){
console.log(result);
client.close();
}
);
});
Database, Collections, Documents: MongoDB
Enteros
About Enteros
IT organizations routinely spend days and weeks troubleshooting production database performance issues across multitudes of critical business systems. Fast and reliable resolution of database performance problems by Enteros enables businesses to generate and save millions of direct revenue, minimize waste of employees’ productivity, reduce the number of licenses, servers, and cloud resources and maximize the productivity of the application, database, and IT operations teams.
The views expressed on this blog are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the opinions of Enteros Inc. This blog may contain links to the content of third-party sites. By providing such links, Enteros Inc. does not adopt, guarantee, approve, or endorse the information, views, or products available on such sites.
Are you interested in writing for Enteros’ Blog? Please send us a pitch!
RELATED POSTS
What Drives Growth in Fashion Tech: Enteros AI SQL, Database Performance Management, and RevOps Intelligence
- 3 March 2026
- Database Performance Management
Introduction The fashion industry has evolved into a digital-first, data-intensive ecosystem. Global apparel brands, luxury houses, direct-to-consumer startups, and fast-fashion giants now compete not just on design and brand—but on digital performance. E-commerce platforms must handle flash sales without crashing. Omnichannel inventory systems must synchronize in real time. AI-driven personalization engines must respond instantly. Pricing … Continue reading “What Drives Growth in Fashion Tech: Enteros AI SQL, Database Performance Management, and RevOps Intelligence”
Who Should Use Enteros for Financial Performance Optimization and Cloud Cost Governance?
Introduction The financial sector is under relentless pressure to grow—without increasing risk, cost, or operational complexity. Digital-first banks are reshaping customer expectations. Capital markets firms demand real-time analytics. Insurers are automating underwriting and claims. Fintech startups scale at cloud speed. Meanwhile, regulatory requirements intensify, margins tighten, and infrastructure costs rise. At the center of all … Continue reading “Who Should Use Enteros for Financial Performance Optimization and Cloud Cost Governance?”
How to Accelerate Banking Growth with Enteros Performance Management and Generative AI
- 2 March 2026
- Database Performance Management
Introduction The banking industry is evolving at unprecedented speed. Digital-first challengers are redefining customer expectations. Legacy institutions are modernizing core systems. Real-time payments, open banking frameworks, AI-driven fraud detection, and personalized financial services are now standard. But beneath every digital innovation lies a critical truth: Banking growth depends on performance. Read more”Indian Country” highlights Enteros … Continue reading “How to Accelerate Banking Growth with Enteros Performance Management and Generative AI”
What Drives Profitability in Fashion Tech: AI SQL, Cost Attribution, and Database Governance with Enteros
Introduction The fashion industry has transformed into a digital-first ecosystem. Global apparel brands, luxury retailers, direct-to-consumer startups, and fast-fashion giants now rely on sophisticated technology stacks to power: E-commerce platforms Omnichannel inventory systems Read more”Indian Country” highlights Enteros and its database performance management platform *Real-time pricing engines Demand forecasting models Supply chain visibility tools Read … Continue reading “What Drives Profitability in Fashion Tech: AI SQL, Cost Attribution, and Database Governance with Enteros”